Conservative Dna Replication Theory. This is repeated in the second round. The parent molecule is unchanged conservative hypothesis.
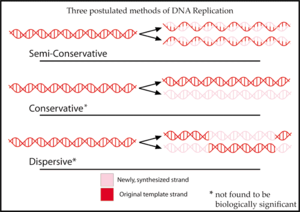
The preferred theory see semiconservative replication proposes that the dna molecule divides to provide two templates for synthesizing the other half of the molecule. Dispersive replication proposed molecules composed of randomized fragments of double old and double new dna. During this process it produces two dna helices from one original dna helix.
Watson and crick figured that this model would result in two new double strands of dna each one with one strand of parent or template dna and one strand of daughter or newly synthesized dna.
During this process it produces two dna helices from one original dna helix. In conservative replication the original dna strands stay associated with each other while the newly made dna forms its own double helix. Watson and crick figured that this model would result in two new double strands of dna each one with one strand of parent or template dna and one strand of daughter or newly synthesized dna. The parent dna molecule breaks into segments and new nucleotides fill in the gaps precisely fragmentation theory.